Review apps
- Tier: Free, Premium, Ultimate
- Offering: GitLab.com, GitLab Self-Managed, GitLab Dedicated
Review apps are temporary testing environments that are created automatically for each branch or merge request. You can preview and validate changes without needing to set up a local development environment.
Built on dynamic environments, review apps provide a unique environment for each branch or merge request.
These environments help streamline the development workflow by:
- Eliminating the need for local setup to test changes.
- Providing consistent environments for all team members.
- Enabling stakeholders to preview changes with a URL.
- Facilitating faster feedback cycles before changes reach production.
If you have a Kubernetes cluster, you can set up review apps automatically using Auto DevOps.
Review app workflow
A review app workflow could be similar to:
%%{init: { "fontFamily": "GitLab Sans" }}%%
flowchart TD
accTitle: Review app workflow
accDescr: Diagram showing how review apps fit into the GitLab development workflow.
subgraph Development["Development"]
TopicBranch["Create topic branch"]
Commit["Make code changes"]
CreateMR["Create merge request"]
end
subgraph ReviewAppCycle["Review app cycle"]
direction LR
Pipeline["CI/CD pipeline runs"]
ReviewApp["Review app deployed"]
Testing["Review and testing"]
Feedback["Feedback provided"]
NewCommits["Address feedback
with new commits"]
end
subgraph Deployment["Deployment"]
Approval["Merge request approved"]
Merge["Merged to default branch"]
Production["Deployed to production"]
end
TopicBranch --> Commit
Commit --> CreateMR
CreateMR --> Pipeline
Pipeline --> ReviewApp
ReviewApp --> Testing
Testing --> Feedback
Feedback --> NewCommits
NewCommits --> Pipeline
Testing --> Approval
Approval --> Merge
Merge --> Production
Configure review apps
Configure review apps when you want to provide a preview environment of your application for each branch or merge request.
Prerequisites:
- You must have the Developer, Maintainer, or Owner role for the project.
- You must have CI/CD pipelines available in the project.
- You must set up the infrastructure to host and deploy the review apps.
To configure review apps in your project:
On the top bar, select Search or go to and find your project.
Select Build > Pipeline editor.
In your
.gitlab-ci.ymlfile, add a job that creates a dynamic environment. You can use a predefined CI/CD variable to differentiate each environment. For example, using theCI_COMMIT_REF_SLUGpredefined variable:review_app: stage: deploy script: - echo "Deploy to review app environment" # Add your deployment commands here environment: name: review/$CI_COMMIT_REF_SLUG url: https://$CI_COMMIT_REF_SLUG.example.com rules: - if: $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH && $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH != $CI_DEFAULT_BRANCHOptional. Add
when: manualto the job to only deploy review apps manually.Optional. Add a job to stop the review app when it’s no longer needed.
Enter a commit message and select Commit changes.
Use the review apps template
GitLab provides a built-in template that’s configured for merge request pipelines by default.
To use and customize this template:
On the top bar, select Search or go to and find your project.
Select Operate > Environments.
Select Enable review apps.
From the Enable Review Apps dialog that appears, copy the YAML template:
deploy_review: stage: deploy script: - echo "Add script here that deploys the code to your infrastructure" environment: name: review/$CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME url: https://$CI_ENVIRONMENT_SLUG.example.com rules: - if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "merge_request_event"Select Build > Pipeline editor.
Paste the template into your
.gitlab-ci.ymlfile.Customize the template based on your deployment needs:
- Modify the deployment script and environment URL to work with your infrastructure.
- Adjust the rules section if you want to trigger review apps for branches even without merge requests.
For example, for a deployment to Heroku:
deploy_review: stage: deploy image: ruby:latest script: - apt-get update -qy - apt-get install -y ruby-dev - gem install dpl - dpl --provider=heroku --app=$HEROKU_APP_NAME --api-key=$HEROKU_API_KEY environment: name: review/$CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME url: https://$HEROKU_APP_NAME.herokuapp.com on_stop: stop_review_app rules: - if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "merge_request_event"This configuration sets up an automated deployment to Heroku whenever a pipeline runs for a merge request. It uses Ruby’s
dpldeployment tool to handle the process, and creates a dynamic review environment that can be accessed through the specified URL.Enter a commit message and select Commit changes.
Stop review apps
You can configure your review apps to be stopped either manually or automatically to conserve resources.
For more information about stopping environments for review apps, see Stopping an environment.
Auto-stop review apps on merge
To configure review apps to automatically stop when the associated merge request is merged or the branch is deleted:
- Add the
on_stopkeyword to your deployment job. - Create a stop job with the
environment:action: stop. - Optional. Add
when: manualto the stop job to make it possible to manually stop the review app at any time.
For example:
# In your .gitlab-ci.yml file
deploy_review:
# Other configuration...
environment:
name: review/${CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME}
url: https://${CI_ENVIRONMENT_SLUG}.example.com
on_stop: stop_review_app # References the stop_review_app job
stop_review_app:
stage: deploy
script:
- echo "Stop review app"
# Add your cleanup commands here
environment:
name: review/${CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME}
action: stop
when: manual # Makes this job manually triggerable
rules:
- if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "merge_request_event"Time-based automatic stop
To configure review apps to stop automatically after a period of time,
add the auto_stop_in keyword to your deployment job:
# In your .gitlab-ci.yml file
review_app:
script: deploy-review-app
environment:
name: review/$CI_COMMIT_REF_SLUG
auto_stop_in: 1 week # Stops after one week of inactivity
rules:
- if: $CI_MERGE_REQUEST_IDView review apps
To deploy and access review apps:
- Go to your merge request.
- Optional. If the review app job is manual, select Run ( ) to trigger the deployment.
- When the pipeline finishes, select View app to open the review app in your browser.
Example implementations
These projects demonstrate different review app implementations:
Other examples of review apps:
Route maps
Route maps let you navigate directly from source files to their corresponding public pages in the review app environment. This feature makes it easier to preview specific changes in your merge requests.
When configured, route maps add contextual links that let you view the review app version of files that match your mapping patterns. These links appear in:
- The merge request widget.
- Commit and file views.
Configure route maps
To set up route maps:
- Create a file in your repository at
.gitlab/route-map.yml. - Define mappings between source paths (in your repository) and public paths (on your review app infrastructure or website).
The route map is a YAML array where each entry maps a source path to a public path.
Each mapping in the route map follows this format:
- source: 'path/to/source/file' # Source file in repository
public: 'path/to/public/page' # Public page on the websiteYou can use two types of mapping:
- Exact match: String literals enclosed in single quotes
- Pattern match: Regular expressions enclosed in forward slashes
For pattern matching with regular expressions:
- The regex must match the entire source path (
^and$anchors are implied). - You can use capture groups
()that can be referenced in thepublicpath. - Reference capture groups using
\Nexpressions in order of occurrence (\1,\2, etc.). - Escape slashes (
/) as\/and periods (.) as\..
GitLab evaluates mappings in order of definition. The first source expression that matches determines the public path.
Example route map
The following example shows a route map for Middleman, a static site generator used for the GitLab website:
# Team data
- source: 'data/team.yml' # data/team.yml
public: 'team/' # team/
# Blogposts
- source: /source\/posts\/([0-9]{4})-([0-9]{2})-([0-9]{2})-(.+?)\..*/ # source/posts/2017-01-30-around-the-world-in-6-releases.html.md.erb
public: '\1/\2/\3/\4/' # 2017/01/30/around-the-world-in-6-releases/
# HTML files
- source: /source\/(.+?\.html).*/ # source/index.html.haml
public: '\1' # index.html
# Other files
- source: /source\/(.*)/ # source/images/blogimages/around-the-world-in-6-releases-cover.png
public: '\1' # images/blogimages/around-the-world-in-6-releases-cover.pngIn this example:
- The mappings are evaluated in order.
- The third mapping ensures that
source/index.html.hamlmatches/source\/(.+?\.html).*/instead of the catch-all/source\/(.*)/. This produces a public path ofindex.htmlinstead ofindex.html.haml.
View mapped pages
Use route maps to navigate directly from source files to their corresponding pages in your review app.
Prerequisites:
- You must have configured route maps in
.gitlab/route-map.yml. - A review app must be deployed for your branch or merge request.
To view mapped pages from the merge request widget:
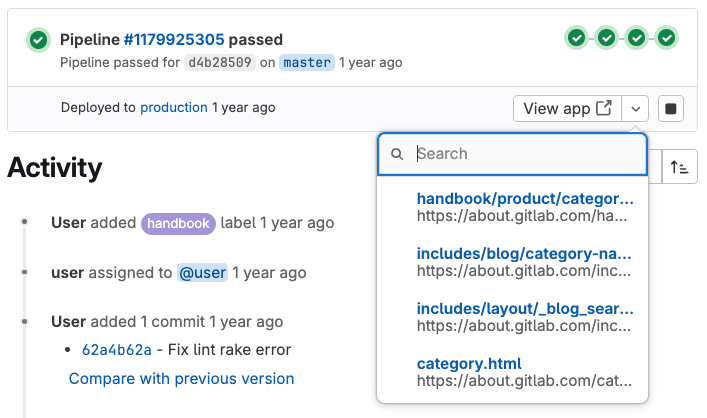
- In the merge request widget, select View app. The dropdown list shows up to 5 mapped pages (with filtering if more are available).
To view a mapped page from a file:
- Go to a file that matches your route map using one of these methods:
- From a merge request: In the Changes tab, select View file @ [commit].
- From a commit page: Select the filename.
- From a comparison: When comparing revisions, select the filename.
- On the file’s page, select View on [environment-name] ( ) in the upper-right corner.
To view mapped pages from a commit:
- Go to a commit that has a review app deployment:
- For branch pipelines: In the left sidebar, select Code > Commits and select a commit with a pipeline badge.
- For merge request pipelines: In your merge request, select the Commits tab and select a commit.
- For merged results pipelines: In your merge request, select the Pipelines tab and select the pipeline commit.
- Select the review app icon ( ) next to a filename that matches your route map. The icon opens the corresponding page in your review app.
Merged results pipelines create an internal commit that merges your branch with the target branch. To access review app links for these pipelines, use the commit from the Pipelines tab, not the Commits tab.