GitHub
You can update GitHub with pipeline status updates from GitLab. The GitHub integration can help you if you use GitLab for CI/CD.
This project integration is separate from the instance-wide GitHub integration and is automatically configured when you import a GitHub project.
Configure the integration
This integration requires a GitHub API token
with repo:status access granted.
Complete these steps on GitHub:
- Go to your Personal access tokens page at https://github.com/settings/tokens.
- Select Generate new token.
- Under Note, enter a name for the new token.
- Ensure
repo:statusis selected and select Generate token. - Copy the generated token to use in GitLab.
Complete these steps in GitLab:
- On the left sidebar, select Search or go to and find your project.
- Select Settings > Integrations.
- Select GitHub.
- Ensure the Active checkbox is selected.
- In Token, paste the token you generated on GitHub.
- In Repository URL, enter the path to your project on GitHub, such as
https://github.com/username/repository. - Optional. To disable static status check names, clear the Enable static status check names checkbox.
- Optional. Select Test settings.
- Select Save changes.
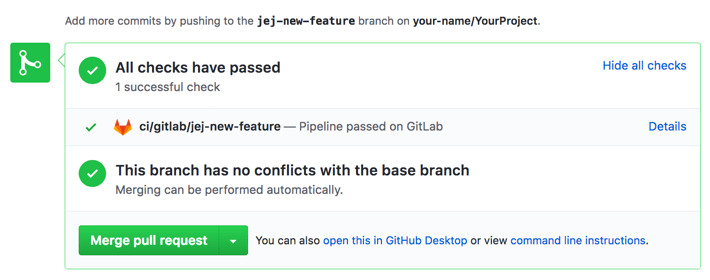
After configuring the integration, see Pipelines for external pull requests to configure pipelines to run for open pull requests.
Static or dynamic status check names
A status check name can be static or dynamic:
-
Static: The hostname of your GitLab instance is appended to the status check name.
-
Dynamic: The branch name is appended to the status check name.
The Enable static status check names option enables you to configure required status checks in GitHub, which need a consistent (static) name to work correctly.
If you disable this option, GitLab uses dynamic status check names instead.